Are Galvanized Raised Beds Safe?
Raised garden beds offer numerous advantages, including improved drainage, better soil control, and easier access for gardeners. Among the various materials used for constructing raised beds, galvanized steel stands out for its durability and affordability. However, concerns regarding the safety of using galvanized steel, specifically due to the potential leaching of zinc into the soil, have led many gardeners to question its suitability for food production.
Understanding Galvanization
Galvanization is a process that coats steel with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. This protective layer significantly extends the lifespan of the steel, making it resistant to rust and weathering. While zinc is an essential micronutrient for plants, excessive amounts can be detrimental. This raises the question of whether galvanized steel raised beds can leach enough zinc to pose a risk to plant health and human consumption.
Potential Risks of Zinc Leaching
Zinc leaching from galvanized steel is a complex issue influenced by several factors, including soil pH, moisture levels, and the type of galvanization used. In highly acidic soils (pH below 6.0), zinc is more readily soluble and thus more likely to leach into the soil. Similarly, consistently wet conditions can accelerate the corrosion process and increase the potential for zinc release.
Types of Galvanization
There are two primary methods of galvanization: hot-dipped galvanization and electro-galvanization. Hot-dipped galvanization involves submerging the steel in molten zinc, resulting in a thicker and more durable coating. Electro-galvanization, on the other hand, uses an electrolytic process to deposit a thinner layer of zinc onto the steel. Hot-dipped galvanization generally offers better corrosion resistance and, consequently, potentially less zinc leaching compared to electro-galvanization.
Evaluating Soil pH and Amendments
Before installing galvanized raised beds, it is crucial to test the soil pH. If the soil is highly acidic, amending it with lime to raise the pH can significantly reduce the risk of zinc leaching. Regular monitoring of soil pH is also recommended to ensure that the soil remains within a safe range for plant growth.
Considering Liner Options
Using a liner within the galvanized raised bed can create a barrier between the soil and the galvanized steel, further minimizing the potential for zinc contamination. Suitable liner materials include heavy-duty plastic sheeting, landscape fabric, or even a layer of cardboard. These liners prevent direct contact between the soil and the galvanized steel, effectively mitigating zinc leaching.
Crop Selection and Rotation
Certain crops are more sensitive to zinc toxicity than others. While leafy greens can accumulate higher levels of zinc, fruiting vegetables generally show less sensitivity. Employing crop rotation can help prevent the buildup of zinc in the soil and minimize the risk of affecting sensitive plants.
Research and Studies on Zinc Leaching
Several studies have investigated the potential for zinc leaching from galvanized steel raised beds. While some studies have indicated a slight increase in soil zinc levels, the levels observed have generally remained within safe limits for plant growth and human consumption. However, further research is ongoing to fully understand the long-term effects and potential risks associated with using galvanized steel in food production.
Alternative Materials for Raised Beds
For gardeners who remain concerned about using galvanized steel, alternative materials are available. These include untreated wood (which requires regular maintenance), cedar or redwood (naturally rot-resistant), composite lumber (made from recycled plastic and wood fibers), and even stone or concrete blocks. Each material presents its own set of advantages and disadvantages regarding cost, durability, and environmental impact.
Long-Term Maintenance and Monitoring
Regardless of the material chosen for raised beds, ongoing maintenance and monitoring are essential for optimal plant health and food safety. Regularly testing soil pH, amending the soil as needed, and observing plants for signs of nutrient deficiencies or toxicities can help ensure a healthy and productive garden.
Making Informed Decisions
The decision of whether or not to use galvanized raised beds ultimately depends on individual circumstances and risk tolerance. By considering factors such as soil pH, liner options, and crop selection, gardeners can make informed decisions that prioritize both practicality and safety. Conducting thorough research and understanding the potential risks associated with galvanized steel is essential for ensuring a thriving and safe garden.

Are Galvanized Steel Garden Beds Safe Epic Gardening

Galvanized Raised Beds Big And Small Kits Diy Options

Galvanized Raised Beds Big And Small Kits Diy Options

5 Misconceptions Of Metal Garden Beds Why They Are Safe Sunnydaze Decor

Raised Garden Beds Galvanized Metal Vs Wood Huw Richards
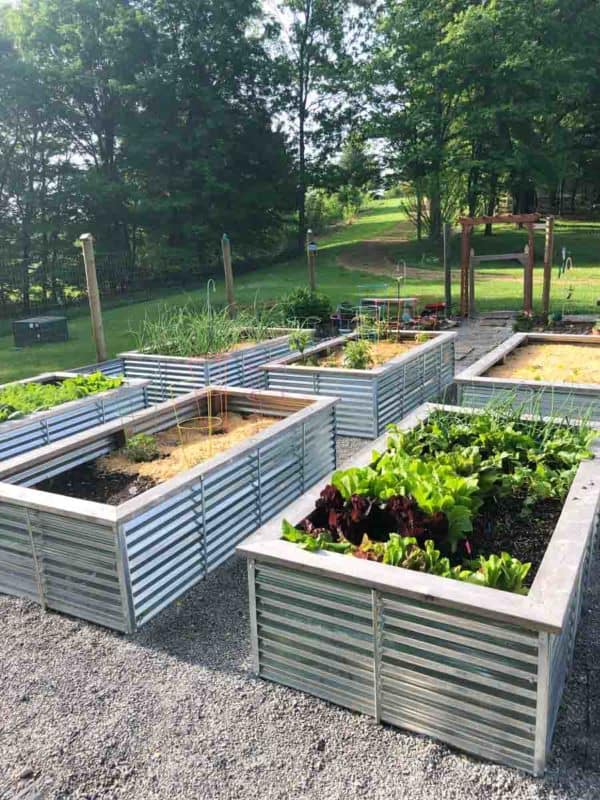

Galvanized Steel Raised Garden Beds Plans Tutorial Growfully

How To Grow Vegetables In A Galvanized Raised Garden Bed Gate

Raised Garden Bed Materials What S Good Epic Gardening

Is It Safe To Use Galvanized Metal For Raised Beds Crate And Basket

Galvanized Raised Beds Big And Small Kits Diy Options